The Role of Kubernetes in Modern Cloud Computing
Deploying a single Docker container to a local machine is straightforward. Managing thousands of containers across a distributed cloud environment, ensuring they communicate effectively, restart upon failure, and scale with demand? That is a different beast entirely.
For software engineers and data scientists, the shift from monolithic architectures to microservices has revolutionized how we build applications. However, this shift introduced significant operational complexity. This is where Kubernetes (K8s) enters the frame.
As the de facto standard for container orchestration, Kubernetes has become the operating system of the modern cloud. But its value extends far beyond basic app deployment. For those working in AI and machine learning, Kubernetes provides the infrastructure necessary to train complex models, manage resource intensive workloads, and deploy scalable solutions that drive business value.
In this article, we will analyze the core architecture of Kubernetes, its pivotal role in cloud computing, and specifically how it empowers high performance AI and data workflows.
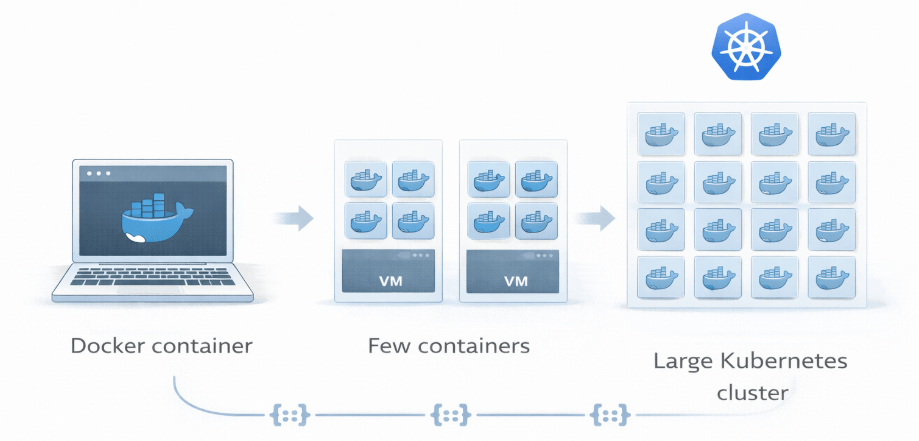
The Evolution from Virtualization to Orchestration
To understand the dominance of Kubernetes, we must look at the infrastructure problems it solves.
Traditionally, organizations ran applications on physical servers. This was inefficient; if one app hogged resources, others suffered. Virtualization (VMs) solved this by isolating environments, but VMs are heavy, requiring a full OS for every instance.
Containers offered a lightweight alternative, bundling code and dependencies without the OS overhead. This made applications portable and fast. However, as developers broke monoliths into hundreds of microservices, they needed a way to manage them.
Kubernetes, originally developed by Google and now maintained by the Cloud Native Computing Foundation (CNCF), acts as the traffic controller. It automates the deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications.
Core Architecture: How Kubernetes Works
At its heart, Kubernetes creates a cluster with a set of worker machines (nodes) that run containerized applications. Here is a breakdown of the essential components you need to understand:
- The Control Plane: The brain of the cluster. It makes global decisions (like scheduling), detects events, and responds to them (like starting up a new pod when one crashes).
- Nodes: These are worker machines (VMs or physical servers). Each node contains the services necessary to run pods.
- Pods: The smallest deployable units of computing that you can create and manage. A pod hosts one or more containers (like Docker containers) that share storage and network resources.
- Services: An abstract way to expose an application running on a set of Pods as a network service. This ensures that even if Pods die and are replaced, the frontend can always find the backend.
Why Kubernetes is Critical for Modern Cloud Comp uting
For intermediate expert developers, the “why” often matters more than the “how.” Kubernetes offers specific advantages that align directly with the needs of scalable, high-performance computing.
1. Seamless Scalability and Auto scaling
One of the most powerful features of Kubernetes is its ability to scale vertically and horizontally.
- Horizontal Pod Autoscaler (HPA): Automatically scales the number of pods in a replication controller or deployment based on observed CPU utilization or custom metrics.
- Cluster Autoscaler: If your pods fail to launch because of insufficient resources, this component adjusts the size of the cluster itself.
For an AI project, this means your infrastructure adapts automatically. During heavy training loads, K8s spins up more nodes; when the job is done, it scales down, ensuring you aren’t paying for idle compute power.
2. High Availability and Self-Healing
In a production environment, downtime is unacceptable. Kubernetes ensure high availability through self-healing mechanisms. If a container fails, K8s restarts it. If a node dies, K8s reschedule the pods to a healthy node. It doesn’t advertise the container to clients until it is ready to serve.
3. Portability Across Environments
Kubernetes standardizes the deployment environment. Whether you are running AWS, Google Cloud, Azure, or on-premises hardware, the K8s’ manifest files remain largely the same. This prevents vendor lock in and allows for hybrid cloud strategies, where sensitive data might stay on prem while public cloud resources are used for burstable compute tasks.
Optimizing AI and Machine Learning Workflows
For our audience of data scientists and AI engineers, Kubernetes is more than just an IT tool; it is an enabler of MLOps.
Training deep learning models requires massive computational power, often involving distributed training across multiple GPUs. Deploying these models for inference requires low latency and high reliability. Here is how K8s supports these specific needs:
Efficient Resource Management (GPU Scheduling)
AI workloads are resource hungry. Kubernetes allows you to specify resource requests and limits (CPU, RAM, and GPU) for each container. Advanced scheduling features ensure that your TensorFlow or PyTorch training jobs are placed on nodes with the appropriate hardware accelerators (like NVIDIA GPUs).
Kubeflow: The AI Toolkit for Kubernetes
Kubeflow is a project dedicated to making deployments of machine learning workflows on Kubernetes simple, portable, and scalable. It provides a native way to run distributed training jobs using frameworks like TensorFlow, PyTorch, and MXNet.
- Jupyter Notebooks: Spin up interactive environments directly in the cluster.
- Pipelines: Build and deploy portable, scalable ML workflows based on Docker containers.
Model Serving at Scale
Once a model is trained, it needs to be deployed. Tools like KServe (formerly KFServing) run on top of Kubernetes to enable serverless inference. This provides “scale to zero” capabilities, meaning you consume zero resources when no one is querying your model, but can instantly scale up to handle thousands of requests per second.
Integration with the Modern Tech Stack
Kubernetes do not exist in vacuums. It integrates seamlessly with the tools you likely already use:
- CI/CD: Tools like Jenkins, GitLab CI, and CircleCI connect directly to K8s clusters to automate the testing and deployment pipeline.
- Monitoring: Prometheus and Grafana are the industry standards for monitoring K8s clusters, giving you real time visibility into performance metrics.
- Infrastructure as Code (IaC): Terraform or Ansible can provision the underlying infrastructure for your Kubernetes clusters, ensuring reproducibility.
Challenges and Considerations
While Kubernetes offers immense power, it also introduces complexity. It is important to acknowledge operational overhead.
- Steep Learning Curve: Understanding manifests, networking policies, and security contexts takes time.
- Day 2 Operations: Upgrading clusters, managing security patches, and troubleshooting networking issues require specialized knowledge.
For many smalls to medium teams, the solution is often Managed Kubernetes Services (like Amazon EKS, Google GKE, or Azure AKS). These services offload the management of the control plane to the cloud provider, allowing your team to focus on deploying applications rather than managing infrastructure.
Leveraging Kubernetes for Your Next Project
Kubernetes has cemented itself as the backbone of modern cloud computing. For AI and data professionals, it offers the performance, scalability, and integration required to move from experimental models to production grade solutions. By abstracting the underlying infrastructure, it allows teams to focus on what matters most: building intelligent algorithms and delivering value to users.
To further improve your development process and build reliable AI powered automation, we recommend auditing your current infrastructure. Are you maximizing your resource utilization? Is your model training pipeline automated? If the answer is no, it may be time to explore how Kubernetes can orchestrate your success.
Leave a comment