The High-Performance Secret: Supercharging React with ASP.NET Core
If you have ever built a data heavy application, you know the sinking feeling of watching a loading spinner spin just a second too long. In the world of enterprise software and AI development, milliseconds matter. While the MERN (MongoDB, Express, React, Node) stack has dominated tutorials for years, seasoned engineers often hit a performance ceiling when data complexity scales.
The problem isn’t usually the frontend; React is excellent at rendering dynamic interfaces. The bottleneck often lies in the backend’s ability to crunch numbers, manage concurrency, and serve payloads efficiently.
This brings us a powerful, often underestimated pairing: React on the frontend and ASP.NET Core on the backend.
This combination isn’t just about mixing Microsoft and Meta technologies; it is about leveraging the raw throughput of compiled C# with the flexible component model of React. In this article, you will learn why this architecture is becoming the go for high performance applications, how the mechanics of this integration work, and how to navigate the complexities of deploying it.
The “Why Now?”: A Convergence of Speed and Scale
Why should a developer comfortable with JavaScript everywhere (Node.js) consider switching context to C#? The answer lies in the architectural shifts we have seen in the last 12 months.
The Performance Gap
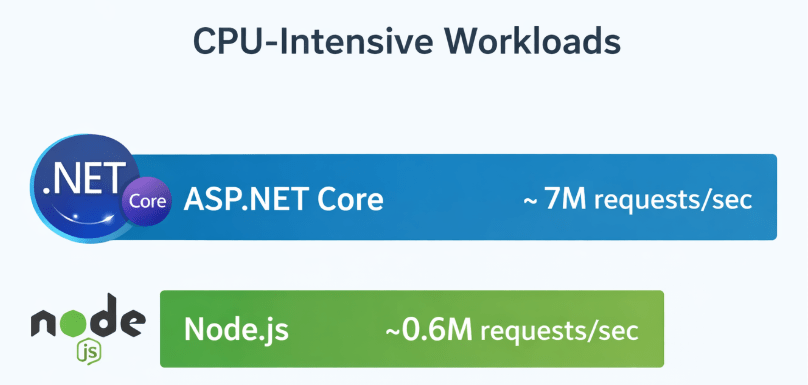
Historically, Node.js was praised for its non-blocking I/O, making it great for I/O heavy tasks. However, recent benchmarks paint a stark picture for CPU intensive tasks common in AI data processing and complex logic. According to independent TechEmpower benchmarks, ASP.NET Core consistently outperforms Node.js, processing over 7 million requests per second compared to Node’s 0.6 million.
The Shift to Type Safety
The industry is moving aggressively toward type safety to reduce runtime errors and improve maintainability. While TypeScript patched this hole for JavaScript, C# offers robust, compile time static typing natively. With ASP.NET Core, you get a mature ecosystem that enforces structure, which is invaluable when your team grows beyond three people.
Cross Platform Maturity
Gone are the days when .NET means “Windows only.” ASP.NET Core is open source and cross platform, running seamlessly on Linux and macOS. This flexibility allows AI developers to deploy high performance backends on the same Linux infrastructure used for training ML models, removing the friction that used to exist between Microsoft stacks and open-source DevOps pipelines.
The Core Mechanism: How the Stack Fits Together
To understand how to build this, you need to visualize the architecture. Think of this stack like a high-end restaurant.
React is in the front of house. It is the ambiance, the menu, and the waiters (UI components) that interact directly with the customer. It needs to be responsive, attractive, and quick.
ASP.NET Core is the kitchen. This is where the heavy lifting happens with chopping ingredients (data processing), cooking (business logic), and plating (API responses).
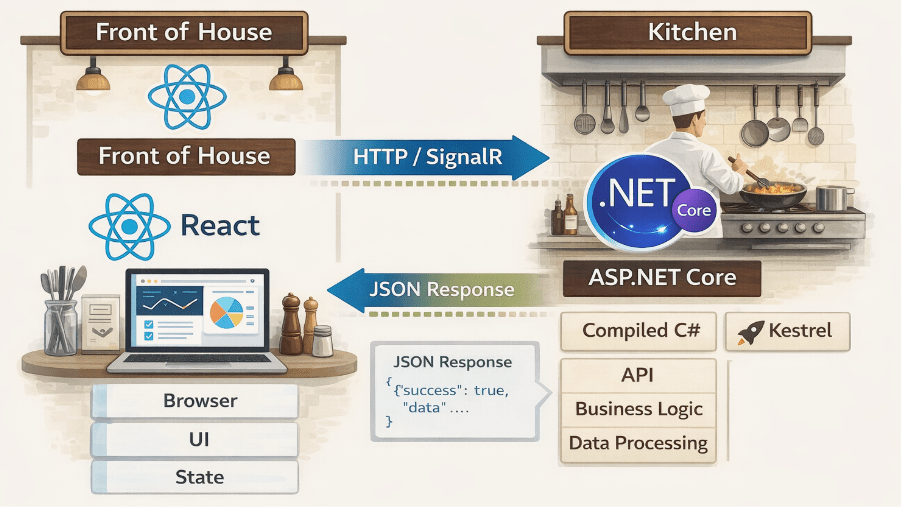
The Architecture Breakdown
In a standard implementation, these two operate as decoupled entities communicating via HTTP/REST or SignalR for real time needs.
- The Client (React): Your React app lives in the browser. It is a Single Page Application (SPA) that manages the display state. When a user requests data say, a forecast from an AI model React fires an asynchronous fetch or axios request.
- The Interface (API Layer): ASP.NET Core Web API receives this request. Unlike interpreted languages that parse code on the fly, your C# code is compiled. The request hits a Controller or a Minimal API endpoint.
- The Engine (Business Logic): The backend processes the request. This might involve querying a SQL database using Entity Framework Core or perhaps invoking an ONNX runtime to serve a machine learning prediction.
- The Response: ASP.NET Core serializes the result into JSON and sends it back. Because Kestrel (the .NET web server) is highly optimized, this serialization happens incredibly fast.
Real Time Capabilities
For AI developers needing real-time feedback like watching a model training loss curve live, ASP.NET Core’s SignalR library is a game changer. It establishes a persistent connection (usually WebSockets) between the React client and the server. This allows the server to push content to the React frontend instantly without the client needing to poll for updates.

Real World Impact: From Theory to Practice
Where does this stack truly shine? It thrives in environments where data integrity and speed are non-negotiable.
Case Study 1: Real Time Financial Trading Platforms
In fintech, dashboards need to handle thousands of updates per second. A React frontend provides the interactive charting library, while an ASP.NET Core backend processes the firehose of market data. The backend can aggregate millions of rows of transaction data, perform thread safe calculations, and stream the summarized view to the React client with minimal latency.
Case Study 2: AI Inference Interfaces
Consider an application that allows radiologists to upload scans for AI analysis.
- React handles the complex drag and drop interface and image visualization.
- ASP.NET Core acts as the robust orchestrator. It receives the secure DICOM file, authenticates the user with enterprise grade security, and dispatches the file to a Python microservice or Azure AI service for processing.
- Once processing is complete, it notifies the user immediately.
Using .NET here allows for seamless integration with Azure’s AI suite, offering scalability that a simpler backend might struggle to match under load.
Challenges and Considerations:
While powerful, this stack introduces complexity that you must be prepared for.
The Context Switching Tax
The most obvious hurdle is the cognitive load of switching languages. A full stack developer on this stack must be proficient in both JavaScript/TypeScript and C#. Context switching between the two syntaxes can slow down development initially compared to a full JS stack where code sharing is trivial.
Setup Complexity
Spinning up a create react app with a Node backend is instantaneous. Setting up a solution with a .NET Web API project, configuring CORS (Cross Origin Resource Sharing) to allow the React app to talk to the backend, and managing two different build pipelines takes deliberate effort.
Hosting Costs
While .NET Core runs on Linux, enterprise grade hosting for high performance applications often leads teams toward Azure. While Azure offers free tiers (like the 10 ASP.NET Core websites for free mentioned in Microsoft documentation), scaling up to production grade instances with separate SQL databases can be more expensive than lightweight serverless Node functions.
Ethics and Privacy
With great power comes great responsibility regarding data. ASP.NET Core makes it easy to integrate with enterprise identity providers (like Azure AD). However, because you are often building monolithic or macro service architectures with this stack, you must be vigilant about not logging sensitive user data (PII) during the high-speed serialization processes.
Conclusion:
The combination of ASP.NET Core and React represents a maturity milestone for full stack development. It moves beyond the “easy to start” philosophy of entirely JavaScript based stacks and embraces a “built to scale” mindset.
For AI developers and software engineers, this stack offers a unique value proposition: the ability to build beautiful, reactive interfaces without sacrificing the backend performance required for modern, data intensive workloads.
Ready to boost your application performance?
Start by building a simple Minimal API in ASP.NET Core and connecting it to a basic React form. Experience the speed of compiled code firsthand. If you are looking to integrate high performance computing with modern UI patterns, this is the architecture to master in 2024.
Leave a comment