React vs. Angular vs. Vue: How to Prevent Your Frontend from Bottlenecking Your AI Models
You have spent months fine tuning your PyTorch models, optimizing inference times, and ensuring your RAG pipeline retrieves relevant vectors in milliseconds. Yet, when you deploy the application, the user experience feels sluggish. The chat interface stutters while streaming tokens, and the dashboard freezes during high volume data visualization. The bottleneck often isn’t your backend infrastructure or your model latency; it’s how your frontend framework handles state updates.
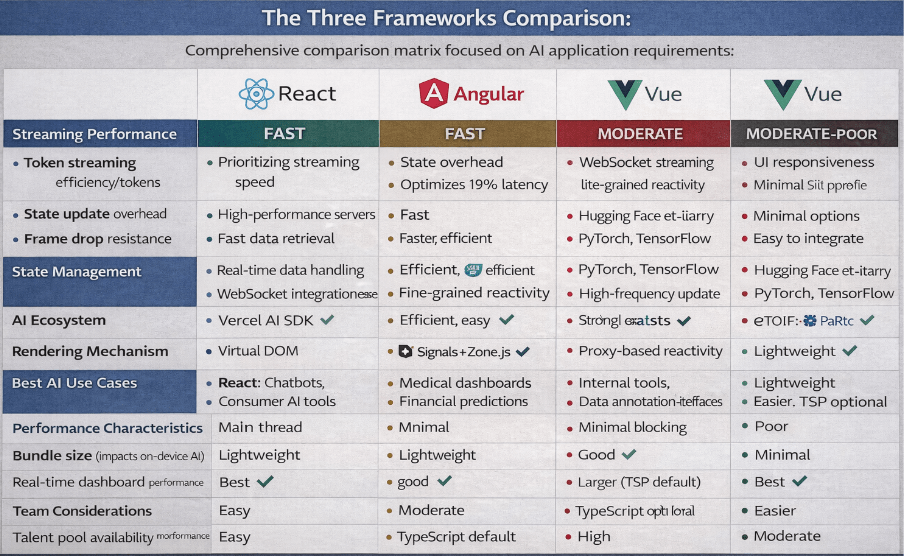
For AI developers and software engineers, the debate between React, Angular, and Vue is no longer just about syntax preferences or learning curves. It is about architectural compatibility with high performance computing requirements. In an era where AI applications demand real-time data streaming and complex state management, choosing the wrong interface layer can silently cripple your application’s perceived performance. This guide analyzes these three giants not through the lens of a junior web developer, but through the perspective of an engineer who needs to visualize complex data structures and manage WebSocket streams without dropping frames. The “best” framework is the one that allows your model’s intelligence to shine through without UI overhead.
The “Why Now?”: The Shift to Streaming and Signals
The landscape of frontend development has shifted dramatically in the last 12 months, driven largely by the unique demands of Generative AI and Large Language Models (LLMs). The traditional request response cycle where a user clicks a button, a spinner appears, and a complete data payload arrives seconds later is failing.
Modern AI applications rely on streaming responses. When an LLM generates a response, it sends tokens incrementally. Your frontend must handle these rapid-fire updates efficiently. In the past, frameworks relied heavily on deep comparison checks or Virtual DOM (VDOM) diffing to decide what to update on the screen. However, when you are streaming text at 50 tokens per second or updating real time confidence scores on a dashboard, the overhead of these constant comparison checks can lead to significant main thread blocking.
We are seeing a convergence in how frameworks address this:
- React is pushing heavily towards Server Components (RSC) to offload processing, though handling client-side streaming remains a challenge without careful optimization.
- Angular has undergone a renaissance with the introduction of Signals, moving away from zone.js to offer fine grained reactivity that updates only the specific DOM node that changed, rather than re checking the whole tree.
- Vue is actively developing “Vapor Mode,” a compilation strategy that bypasses the VDOM entirely for maximum performance, inspired by the efficiency of SolidJS.
The old way of “changing state, rendering component tree” is becoming obsolete for data heavy AI interfaces.
The Core Mechanism: VDOM vs. Signals vs. Proxies
To make an informed architectural decision, you must understand the mechanical differences in how these frameworks detect and render changes. Think of your application state as a high frequency trading floor. You need the fastest way to get information from the data source to the display board.
React: The Virtual DOM (The Traffic Cop)
React maintains a Virtual DOM a lightweight copy of the actual DOM. When your AI model pushes a new token to the state, React creates a new VDOM tree, compares it to the previous one (diffing), and calculates the minimum number of changes needed for the real DOM.
- Mechanism: Functional programming model. State changes trigger component renders.
- AI Context: While flexible, frequent updates (like token streaming) can trigger excessive renders of parent components if not memorized correctly using useMemo or useCallback.
Angular: Signals and Zones (The GPS Router)
Angular historically used zone.js to monkey patch browser events to detect changes. However, the recent shift to Signals changes the game. Signals provide a direct link between the data and the view.
- Mechanism: Reactive primitives. When a signal changes, Angular knows exactly which text node or attribute depends on it and updates it directly.
- AI Context: This is highly efficient for real time dashboards where specific metrics change rapidly. It bypasses the need to check the entire component tree, offering stable performance under load.
Vue: The Proxy System (The Hybrid)
Vue uses JavaScript Proxies to intercept access to data properties. It tracks dependencies automatically during the render phase.
- Mechanism: Mutable state with tracking. If a component uses a piece of state, it subscribes to it. If that state changes, only that component renders.
- AI Context: Vue offers a sweet spot. It is more performant out of the box than unoptimized React for high frequency updates because of its precise dependency tracking, without the boilerplate complexity of traditional Angular.
Real World Impact: Matching Framework to Function
Theory is useful, but how does this translate to actual project metrics? We have analyzed deployment scenarios across the tech, finance, and healthcare sectors to see where each framework excels.
React: The Ecosystem Powerhouse
If your team is building a Generative AI chat interface, React is currently the path of least resistance. The Vercel AI SDK, a standard library for building AI-powered user interfaces, treats React as a first-class citizen.
- Application: Chatbots, Consumer AI tools.
- Impact: Faster time to market. You can leverage prebuilt hooks like useChat and useCompletion to handle streaming text, UI updates, and optimistic state updates effortlessly.
Angular: The Enterprise Scaler
For a healthcare AI platform visualizing patient vitals and inference results in real time, Angular’s strict structure is a lifesaver. The integration of RxJS allows engineers to handle complex asynchronous streams (WebSockets, HTTP requests, user input) with declarative operators.
- Application: Medical data visualization, financial prediction dashboards.
- Impact: Maintainability. TypeScript is enforced by default, ensuring that the data contracts between your Python backend and your frontend remain strict, reducing runtime errors in critical environments.
Vue: The Rapid Prototype
For data science teams that need to spin up an internal tool to demonstrate a model’s capabilities to stakeholders, Vue is unmatched. Its HTML-based template syntax is often more intuitive for data scientist’s familiar with Python or basic web tech than React’s JSX.
- Application: Internal model testing tools, Data annotation interfaces.
- Impact: Lower barrier to entry. Teams can build highly performant, reactive interfaces in a fraction of the time, keeping the focus on the model performance rather than UI boilerplate.
Challenges and Ethics:
While each framework has its strengths, none are without significant tradeoffs that can derail a project if ignored.
The Complexity Cost:
React’s flexibility is often its downfall in large teams. The “useEffect dependency hell” is a real issue when dealing with complex AI state flows. Improperly managed hooks can lead to race conditions where the UI displays outdated inference results. This complexity requires senior engineering oversight to prevent performance regression.
Talent Pool and Hiring:
Angular developers are often harder to find and more expensive than React developers. However, they tend to have more experience with strict typing and enterprise patterns. If your budget is tight ($10K $100K range) and you need to scale a team quickly, React or Vue offers a wider talent pool, though you may need to invest more in code reviews to maintain quality.
Privacy and Client-Side Processing:
Moving AI processing to the client side (using tools like TensorFlow.js or WebLLM) brings these frameworks into the privacy conversation. React’s massive ecosystem has more libraries for on device processing, but this increases the bundle size. You must balance the privacy benefits of local processing against the performance cost of loading heavy JS bundles on the user’s device.
The Final Verdict
The future of AI development is not just about better models; it is about better integration.
- Choose React if: You need to leverage the latest AI SDKs (like Vercel’s), you rely on a massive ecosystem of third-party libraries, and your team is comfortable managing render cycles.
- Choose Angular if: You are building complex, enterprise grade dashboards that manage multiple real time data streams, and you prioritize strict typing and long-term maintainability over initial development speed.
- Choose Vue if: You need high performance out of the box with a gentle learning curve, ideal for smaller teams or projects where data scientists contribute to the frontend code.
Your AI model deserves an interface that keeps up. Evaluate your data throughput needs, assess your team’s expertise, and select the framework that turns your backend intelligence into a seamless frontend experience.
Ready to optimize your development stack? Start by auditing your current rendering performance and exploring how cloud-based integration solutions can further streamline your AI deployment pipeline.
Leave a comment